Picture this: the warm sun on your face, a gentle breeze, and a clear blue sky. It’s a perfect day to step outside and soak in the sunlight. But then you wonder — how much sun is too much? Or am I getting enough for my body’s needs?

The truth is, sunlight is essential for your health, but overdoing it can lead to serious risks. Finding the right balance is key. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about healthy sun exposure, from the benefits of sunlight to the risks of too much UV radiation. By the end, you’ll know how to enjoy the sunshine safely and keep your skin and body happy.
Why Sun Exposure is Important for Your Health
Sunlight and Vitamin D
Your body needs sunlight to produce vitamin D — a nutrient that’s vital for strong bones, immune support, and overall well-being. Without enough vitamin D, you might experience fatigue, weaker bones, or even depression. According to research by Harvard University, people with moderate sun exposure are less likely to suffer from vitamin D deficiencies compared to those who avoid sunlight entirely.
Here’s why vitamin D is so important:
- Strong bones: It helps your body absorb calcium and maintain bone health.
- Immunity boost: Supports your immune system, reducing the risk of certain infections.
- Mood improvement: A lack of vitamin D has been linked to mood disorders like Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
Sunlight Boosts Mental Health
Ever notice how a sunny day instantly lifts your spirits? That’s because sunlight helps your brain release serotonin — a chemical that makes you feel happy and calm. Studies from the University of Michigan show that regular exposure to natural light can reduce stress and improve your overall mood.
Regulating Your Sleep Cycle
Sunlight plays a big role in your body’s natural clock, also known as your circadian rhythm. Getting enough sunlight during the day — especially in the morning — helps you sleep better at night. It signals to your brain when it’s time to be awake and when it’s time to rest.
The Risks of Too Much Sun Exposure
While the sun has its benefits, overexposure can lead to problems. Understanding the risks is the first step to staying safe.
Skin Damage and Premature Aging
Too much UV radiation damages your skin over time, causing wrinkles, fine lines, and dark spots. Prolonged exposure can even alter your DNA, leading to long-term skin issues.
- Fun Fact: According to the American Academy of Dermatology, 90% of visible skin aging is caused by sun damage — not just growing older!
Increased Risk of Skin Cancer
This is one of the biggest concerns with excessive sun exposure. UV rays can damage the DNA in your skin cells, increasing the risk of skin cancers like melanoma. The Skin Cancer Foundation states that wearing sunscreen daily can cut your risk of developing melanoma by up to 50%.
Eye Problems
Too much sun exposure isn’t just harmful to your skin — it can also affect your eyes. UV rays may lead to cataracts or macular degeneration, which can harm your vision over time.
How Much Sun Exposure Is Healthy?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer because it depends on a few factors, including your skin type, where you live, and the time of day.
Factors That Affect Healthy Sun Exposure
- Skin tone: Lighter skin produces vitamin D faster than darker skin but is also more prone to sunburn.
- Location: UV rays are stronger near the equator and at higher altitudes.
- Time of day: The sun’s rays are strongest between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., so aim for early-morning or late-afternoon exposure.
- Season: Sunlight is more intense in summer than in winter.
General Guidelines for Safe Sun Exposure
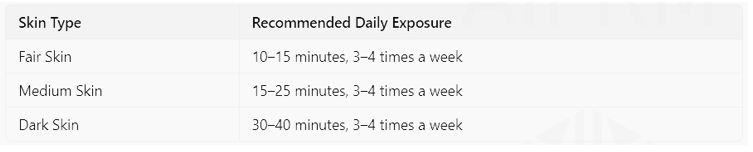
Here’s a quick guide based on skin type:
These recommendations assume moderate UV levels, so adjust your time if the UV index is high.
How to Protect Yourself from Harmful UV Rays
Use Sunscreen (Your Best Friend)
- Always apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher.
- Reapply every two hours, especially if you’re swimming or sweating.
- Make it part of your daily routine — even on cloudy days.

A study by the University of Sydney found that consistent sunscreen use significantly reduces the risk of skin cancer while still allowing for vitamin D production.
Wear Protective Clothing
- Wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses shield sensitive areas.
- Long-sleeved shirts and lightweight fabrics can protect your skin while keeping you cool.
Seek Shade During Peak Hours
If you’re outdoors between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., find some shade to limit your exposure to direct sunlight.
Sun Exposure Tips for Kids and Seniors
For Kids
Children’s skin is delicate and burns easily. Ensure they wear sunscreen, hats, and UV-protective clothing when playing outdoors.
For Seniors
Older adults often need more sunlight to maintain healthy vitamin D levels. However, since aging skin is more vulnerable, it’s important to balance exposure with protection.
Eat Your Way to Better Sun Protection
Certain foods can help protect your skin from the inside out. Nutrients like beta-carotene, vitamin E, and omega-3s are particularly beneficial.

Add these to your meals to support your skin’s health and resilience.
Practical Tips for Safe and Healthy Sun Exposure
- Track the UV Index: Check weather apps for the daily UV index to plan your time outdoors.
- Embrace Technology: Apps like “SunSmart” can remind you to reapply sunscreen or warn you about high UV levels.
- Build a Routine: Incorporate short periods of sun exposure into your daily life rather than long, unprotected stretches.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Balance
When it comes to sun exposure, balance is everything. A little sunshine is great for your body and mind, but too much can harm your skin and health. By following these tips — using sunscreen, eating the right foods, and limiting time in intense sunlight — you can enjoy the benefits of the sun while staying safe.
So next time you step outside, don’t be afraid to bask in the sunshine — just do it wisely!
FAQs About How Much Sun Exposure Is Healthy
1. How much sun do I need daily?
About 10–30 minutes, depending on your skin type and the UV intensity.
2. Can I get vitamin D through a window?
No, UVB rays (needed for vitamin D) can’t penetrate glass.
3. What’s the best time to get sunlight?
Early morning or late afternoon is best when the UV rays are less intense.
4. Do I need sunscreen if I’m only outside for a few minutes?
Yes, even short periods of sun exposure can cause skin damage over time.
5. What foods help protect my skin from the sun?
Foods rich in beta-carotene, vitamin E, and omega-3s can support skin health and reduce damage.
Ready to enjoy the sunshine while staying safe? Start making these simple changes today!



